
Written by Gaby
Edited on
28 October 2024
·
16:22
How do you choose the power of an electric heater?
The power of an electric heater indicates how powerful the heater is and how much energy it consumes. How much power your electric heater needs depends on the size and insulation of the room you're heating. In this article, we'll explain how much power a heater needs to heat your room.

Electric heater power
The power indicates how powerful the heater is. An electric heater with 2000W of power can heat a larger room than a heater with 100-0W of power. To compare electric heaters, we use the power to calculate the surface area the heater can heat. We distinguish well and poorly insulated rooms, because you need more power to heat a poorly insulated room than a well-insulated room.
Difference in power per insulation level

Poor insulation: 50W
Was your house built before 1975, does it have thin layers of insulation, single-paned glass or a cat flap that opens often, for example? We consider this poor insulation, so the heater needs 50W to heat 1m3. This means that a 1000W heater can heat 20m3 in this case.
Good insulation: 35W
Do you live in a newly built house or a house with thick layers of insulation, with at least double-paned windows and few air holes? The heater needs 35W to heat 1m3. This means that a 1000W heater can heat 28.5m3 in this case.
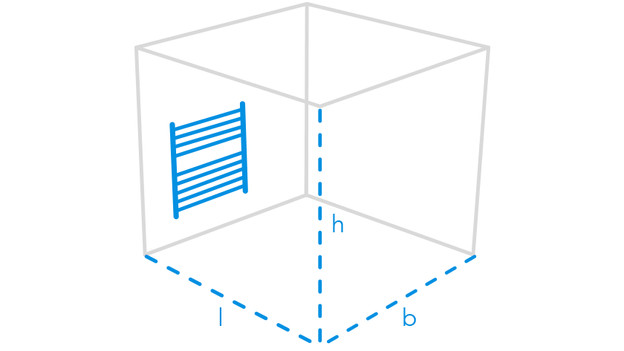
Calculate the power for your room
Want to know how much power a heater needs for your room? First, calculate how many cubic meters the room is. You can do this with the following sum: length x width x height.
For example: 6m x 5m x 2.5m = 75m3
Multiply this result by the power that corresponds to the insulation of your room.
Example of poor insulation: 75m3 x 50W = 3750W So you need 3750W of power to heat this room.
Article by Gaby
Heater Expert.
