Filament 3D printer vs resin 3D printer
Comparison filament 3D printer and resin 3D printer
| Filament 3D printer | Resin 3D printer | |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) / Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) | Stereolithography (SLA) |
| Printing material | Filament | Resin |
| Costs printing material | Low | Higher |
| Accuracy | Lower | High |
| Recommended for designs | Prototypes, utensils | Miniatures, models |
Technology

Filament 3D printer: FFF technology
A filament 3D printer uses the Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) technology. This technology is also called Fused Deposition Modeling (FMD). It means that the printer uses a thermoplastic that's called filament. This filament is supplied to the printhead. The printhead then melts the filament and burns it layer by layer. Most 3D printers have 1 printhead, but there are also 3D printers with 2 printheads. That way, you can print your design with 2 colors or materials.

Resin 3D printer: SLA technology
A resin 3D printer doesn't use thermoplastic, it uses resin. This is a liquid material made or crushed stone and plastic. You pour this material in a container that's on an LCD screen. A UV light then lights up the screen via the bottom. This way, it hardens your design layer by layer and pulls it out of the resin. This is called the stereolithography (SLA) technology. This allows you to make smaller and very accurate prints.
Performance

Filament 3D printer: larger prints and prototypes
A filament 3D printer usually has a larger printing surface than a resin 3D printer. This allows you to make larger prints, such as prototypes and utensils. The prints are less accurate and the layers of the filament often remain visible. Filament 3D prints are sturdier than resin 3D prints, depending on the type of filament you use. There are different types of filament with different properties. ABS filament can take a beating, while PLA is more fragile, for example.
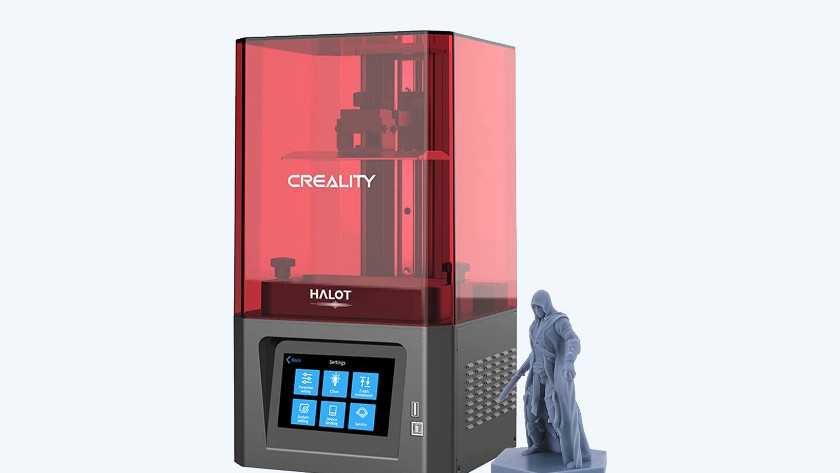

Resin 3D printer: small, very accurate prints
With resin 3D printers, you can mostly make smaller objects with lots of details. Miniatures and models, for example. With a resin print, the layers are so thin that you can hardly see them. Once your design is printed, it still needs to harden. You can do this with direct sunlight or with a special machine, such as the Anycubic Wash & Cure 2.0. Most resin materials can't withstand sunlight and are more fragile than filament.
Costs

Filament 3D printer: affordable filament
There are filament 3D printers in different price ranges. You can get a starter model for less than € 300. An example of a good starter model is the Creality Ender 3 V2. Th Anycubic brand also makes budget filament 3D printers. The Snapmaker 2.0 filament printers are more expensive models. These 3D printers have more functions and are suitable for more filament types. Filament is more affordable, compared to resin. You can buy 1kg of budget PLA filament for € 13.
Resin 3D printer: expensive printing material
Resin 3D printers have become much more affordable in the past few years. Resin 3D printers were mostly being used by professionals. Now, they're also available to hobbyists. Brands like Anycubic and Creality have starter models for personal use. These models range between € 300 and € 800. Per kilo, resin is more expensive than filament. On the other hand, a resin 3D printer makes smaller prints. So the resin does last longer.
Conclusion
With a filament 3D printer, you can make larger and less accurate 3D prints. This makes a filament 3D printer suitable for making prototypes and utensils. Do you want to make smaller and more accurate prints? Choose a resin 3D printer. This allows you to make mall objects with lots of details, such as miniatures and models.


